Medikamentbeschichteter Ballonkatheter
Pantera® Lux®
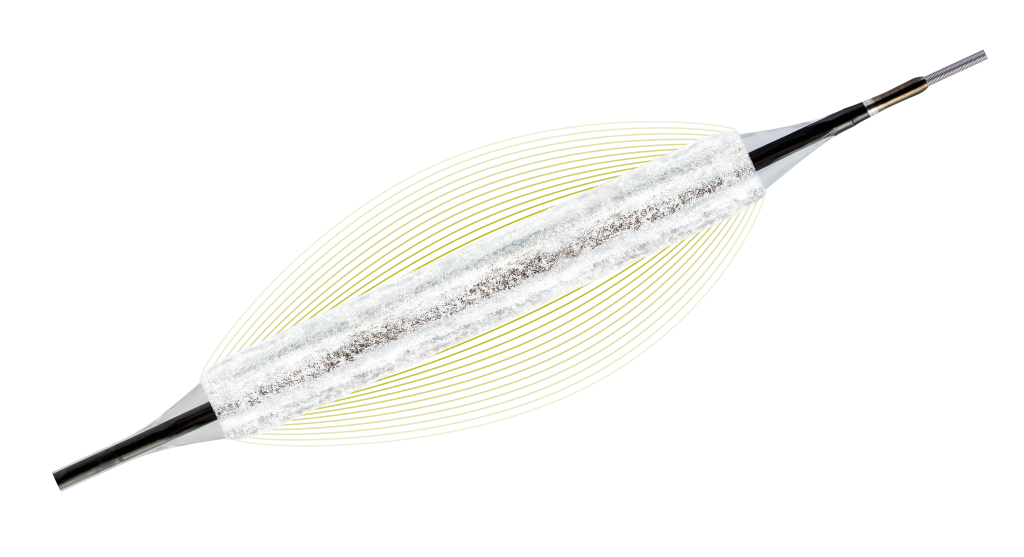




Indiziert für die Ballondilatation bei der In-Stent-Restenose, in De-novo-Läsionen, bei akutem oder drohendem Gefäßverschluss und der Behandlung der Mikroangiopathie.*
The Pantera® Lux® DCB with its Lux® coating is part of the Lux® family of Paclitaxel-coated balloons from BIOTRONIK.
1. Hehrlein C. et al. Cardiovasc .Revasc .Med. 2012 Sep; 13(5): 260-4. 2. Toelg R. et al. EuroIntervention 2014 Sep; 10(5): 591-9. 3. Naber C.K. EuroPCR 2016, mündliche Präsentation. BIOLUX RCT Clinical performance of the Pantera Lux Paclitaxel coated balloon vs. drug-eluting Orsiro hybrid stent system in patients with in-stent restenosis: a randomized controlled trial. 4. Kufner et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv 2017;10: 1332 -40, Clinical trials.gov, NCT01632371. 5. Garcia- Touchard et al. EuroIntervention. 2017 Jan 20;12(13):1587-1594. NCT01839890. 6. Vos N. S. et al. EuroIntervention 2014;10:584-590. 7. Jim M. H. AsiaPCR 2014, mündliche Präsentation: Six-month Angiographic Restudy of Paclitaxel-Eluting balloon kissing in Dealing with side branch Ostial Narrowing (SARPEDON). 8. Worthley S. et al. Cardiovasc. Revasc .Med. 2015; 16: 413-417. 9. Radke P. et al. EuroIntervention. 2011 Oct; 7(6): 730-7. 10. BIOTRONIK Daten im Archiv. 11. BIOTRONIK Daten im Archiv, im Vergleich zu Hauptwettbewerbern. *Indikation gemäß Gebrauchsanweisung. Die Indikationen können in Ländern, die die CE-Kennzeichnung nicht anerkennen, anders sein. SeQuent ist eine eingetragene Handelsmarke von der B. Braun Group of Companies. ELUTAX ist eine eingetragene Handelsmarke von Aachen Resonance. IN.PACT ist eine eingetragene Handelsmarke von der Medtronic Group of Companies. DIOR ist eine eingetragene Handelsmarke von Eurocor. Pantera ist eine Marke oder eingetragene Marke der Unternehmensgruppe BIOTRONIK.
1. Hehrlein C. et al. Cardiovasc .Revasc .Med. 2012 Sep; 13(5): 260-4. 2. Toelg R. et al. EuroIntervention 2014 Sep; 10(5): 591-9. 3. Naber C.K. EuroPCR 2016, mündliche Präsentation. BIOLUX RCT Clinical performance of the Pantera Lux Paclitaxel coated balloon vs. drug-eluting Orsiro hybrid stent system in patients with in-stent restenosis: a randomized controlled trial. 4. Kufner et al. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv 2017;10: 1332 -40, Clinical trials.gov, NCT01632371. 5. Garcia- Touchard et al. EuroIntervention. 2017 Jan 20;12(13):1587-1594. NCT01839890. 6. Vos N. S. et al. EuroIntervention 2014;10:584-590. 7. Jim M. H. AsiaPCR 2014, mündliche Präsentation: Six-month Angiographic Restudy of Paclitaxel-Eluting balloon kissing in Dealing with side branch Ostial Narrowing (SARPEDON). 8. Worthley S. et al. Cardiovasc. Revasc .Med. 2015; 16: 413-417. 9. Radke P. et al. EuroIntervention. 2011 Oct; 7(6): 730-7. 10. BIOTRONIK Daten im Archiv. 11. BIOTRONIK Daten im Archiv, im Vergleich zu Hauptwettbewerbern. *Indikation gemäß Gebrauchsanweisung. Die Indikationen können in Ländern, die die CE-Kennzeichnung nicht anerkennen, anders sein.
Technische Daten
| Wirkstoff-freisetzender Ballonkatheter | |
|---|---|
| Kathetertyp | Medikamentbeschichteter Ballonkatheter |
| Empfohlener Führungskatheter | 5F (min. I.D. 0,056”) |
| Läsionseintrittsprofil |
0,017” |
| Führungsdrahtdurchmesser | 0,014” |
| Arbeitslänge des Katheters |
140 cm |
| Ballonfaltung |
3-fach |
| Ballonmarker | Platin-Iridium |
| Schaftmarkierung, brachial | 92 cm von der Spitze |
| Schaftmarkierung, femoral |
102 cm von der Spitze |
| Proximaler Schaftdurchmesser |
2,0 F |
| Distaler Schaftdurchmesser | 2,5 F (ø 2,0 - 3,5 mm), 2,6F (ø 4,0 mm) |
| Nominaldruck (NP) | 7 atm |
| Angegebener Berstdruck (RBP) | 13 atm (ø 2,0 - 3,5 mm); 12 atm (ø 4,0 mm) |
| Beschichtung | |
|---|---|
| Wirkstoff | Paclitaxel |
| Wirkstoffdosis | 3,0 μg/mm² |
| Applikationsmatrix | Paclitaxel und Butyryl-tri-hexylcitrat (BTHC) |
| Beschichteter Bereich | Zylindrischer Abschnitt des Ballons, über den proximalen und distalen Ballonmarker hinausreichend |
Compliance - Tabelle
| Ballondurchmesser x Länge (mm) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominaldruck | atm5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |||||||||||||
| (NP) | ø (mm) | 2,00 | 2,50 | 3,00 | 3,50 | 4,00 | |||||||||||||
| Angegebener Berstdruck | atm5 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | |||||||||||||
| (RBP) | ø (mm) | 2,26 | 2,82 | 3,48 | 4,11 | 4,59 | |||||||||||||
Bestellinformationen
| 2,0 | 365110 | 365111 | 365112 | 365113 | 365114 | |||||||||
| 2,5 | 365120 | 365121 | 365122 | 365123 | 365124 | |||||||||
| 3,0 | 365125 | 365126 | 365127 | 365128 | 365129 | |||||||||
| 3,5 | 365130 | 365131 | 365132 | 365133 | 365134 | |||||||||
| 4,0 | 365135 | 365136 | 365137 | 365138 | 365139 | |||||||||