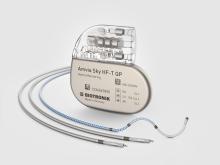
Rivacor 5 DR-T/VR-T DX/VR-T
Verbesserte Behandlung und geringeres Risiko über einen Zeitraum von bis zu 15 Jahren9
Für Patienten mit Arrhythmien kann die ICD-Therapie ein lebenswichtiges Sicherheitsnetz darstellen. In diesem Zusammenhang ist es besonders wichtig, langfristig Risiken zu minimieren und die Lebensqualität zu verbessern. Genau dafür wurden die brandneuen, kleineren und einfacher programmierbaren ICD-Systeme Rivacor 7 mit einer Laufzeit von bis zu 15 Jahren konzipiert9 – Optimierung der Therapie, wann und wo es wichtig ist. In Kombination mit der Home-Monitoring-Technologie können AF-Episoden früher erkannt14 und so die Zahl inadäquater Schocks und Krankenhausaufenthalte reduziert werden19. All dies wurde in klinischen Studien belegt.
Produkt-Highlights
BIOshape. Ultraflaches ICD (10 mm)
ICDs der Familie Rivacor sind klein und flach– mit nur 10 mm Dicke – und sie haben eine schlanke,elliptische und körperfreundliche BIOshape-Form4
15 Jahre Laufzeit. 10 Jahre Garantie.
ICDs der Familie Rivacor haben eine verlängerte Batterielaufzeit von bis zu 15 Jahren1, mit 10 Jahren Vollgarantie
DX-Technologie
Alle genannten Vorteile sind auch mit der einzigartigen DX-Technologie verfügbar, die mit einer einzigen Elektrode eine vollständige atriale Diagnostik ermöglicht
Downloads und weitere Links
Kontaktieren Sie uns
Referenzen
1 Contoured housing; Acticor/Rivacor VR: 60x61.5x10 mm; 30 ccm
2 as part of an MR conditional system
3 Post-Market observation; interim-analysis, December 21, 2018. Data on file.
4 Device shape analysis, February 2019. Data on file.
5 Post-Market observation; interim-analysis, December 21, 2018. Data on file.
6 Post-Market observation; interim-analysis, December 21, 2018. Data on file.
7 Device shape analysis, February 2019. Data on file.
8 Post-Market observation; interim-analysis, December 21, 2018. Data on file.
9 Single-Chamber ICD Standard conditions. Data on file (service time calculation)
10 Acticor/Rivacor Single-Chamber ICD @ 60 ppm, 15% pacing, 2.5V, 500 Ohms: Medtronic 3T FBS; VISIA AF (EVERA; MIRRO) MRI S VR SureScan: 10.7 years (MDT IFU) vs Acticor 7 VR-T ProMRI: 14.9 years. Competitor device manuals as of Nov. 2018
11 Polyzos KA, Konstantelias AA, Falagas ME, Risk factors for cardiac implantable electronic device infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Europace (2015) 17, 767-777.
12 Fact file: Cardiac Imaging with MRI, CT and Nuclear Techniques British Heart Foundation. January 2010.
13 When patients are monitored by BIOTRONIK Home Monitoring. See ProMRI(R) manual for all details.
14 Varma N et al. Efficacy and Safety of Automatic Remote Monitoring for Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Follow-Up: The Lumos-T Safely Reduces Routine Office Device Follow-Up (TRUST) Trial. Circulation, 2010;122: 325 – 332.
15 Guedon-Moreau L et al. Decreased delivery of inappropriate shocks achieved by remote monitoring of ICD: a substudy of the ECOST trial. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 25 (2014), 763-770.
16 Guedon-Moreau L et al. Decreased delivery of inappropriate shocks achieved by remote monitoring of ICD: a substudy of the ECOST trial. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 25 (2014), 763-770.
17 Varma N et al. Efficacy and Safety of Automatic Remote Monitoring for Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Follow-Up: The Lumos-T Safely Reduces Routine Office Device Follow-Up (TRUST) Trial. Circulation, 2010;122: 325 – 332.
18 Schwab JO et al. Clinical Course of Dual-Chamber Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Recipients followed by Cardiac Remote Monitoring: Insights from the LION Registry. BioMed Research International, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3120480.
19 Guedon-Moreau L et al. Decreased delivery of inappropriate shocks achieved by remote monitoring of ICD: a substudy of the ECOST trial. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 25 (2014), 763-770.
20 Guedon-Moreau L et al. Decreased delivery of inappropriate shocks achieved by remote monitoring of ICD: a substudy of the ECOST trial. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 25 (2014), 763-770.
21 Ricci R P et al. Long-term patient acceptance of and satisfaction with implanted device remote monitoring. Europace (2010) 12, 674-679.
22 Ricci R P et al. Long-term patient acceptance of and satisfaction with implanted device remote monitoring. Europace (2010) 12, 674-679.
23 Hindricks G et al. Implant-based multiparameter telemonitoring of patients with heart failure (IN-TIME): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2014; 384 (9943): 583–590
24 vs. 55% - Crossley G H et al. The CONNEXT (Clinical Evaluation of Remote Notification to Reduce Time to Clinical Decision) Trial. JACC. 2011; 57(10):1181-1189 [for bar chart comparison only]
25 Ricci R P et al. Long-term patient acceptance of and satisfaction with implanted device remote monitoring. Europace (2010) 12, 674-679.
26 Performance analysis. Data on file, 2018
27 Performance analysis. Data on file, 2018
28 Kurt M et al. Avoiding inappropriate therapy of single-lead implantable cardioverter defibrillator by atrial-sensing electrodes. Journal of Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018; 29(12): 1682-1689