Product Features
- CRT Optimization
- ATP Optimization
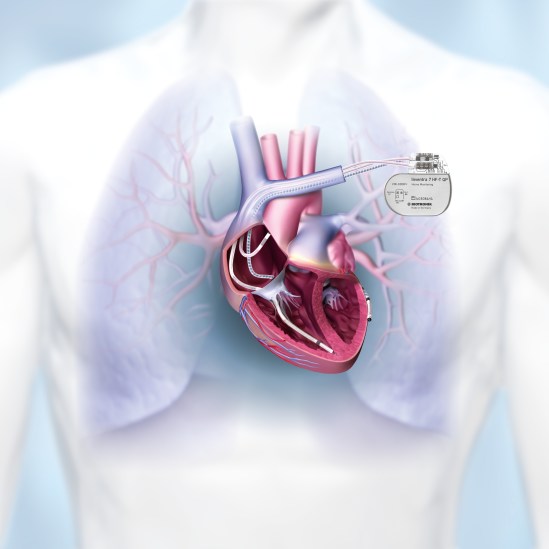
- DX System
- Closed Loop Stimulation
- BIOTRONIK Home Monitoring
- Highly Competitive Longevity
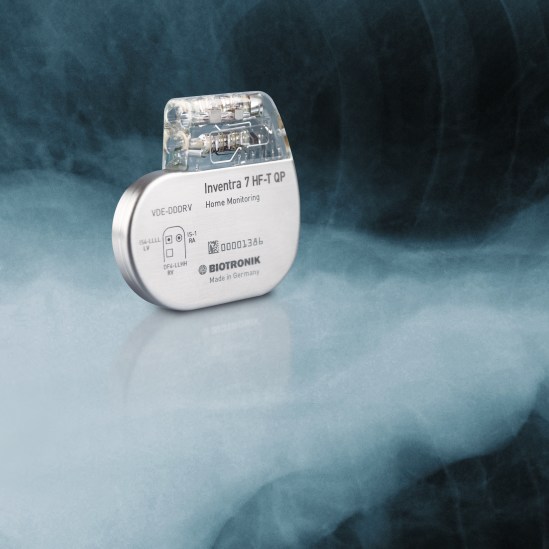
Product Details

BIOTRONIK Home Monitoring®

Closed Loop Stimulation
1 Healey, Jeff S. et al. American Heart Journal, 2012. 164(2).
2 Lin, EF; Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 2013. 36(2).
3 Napp A et al. European Heart Journal. 2010. 31.
4 Shinlapawittayatorn K et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology. 2006. 17(3).
5 Keyser A et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery. 2013. 8(77).
6 Lubiński A et al. Kardiologia Polska. 2005. 62(4).
7 Al-Ahmad A et al. Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators: An Expert’s Manual, Minneapolis, USA. Cardiotext Publishing; 2010.
8 Russo AM et al. Heart Rhythm Journal. 2005. 2(5).