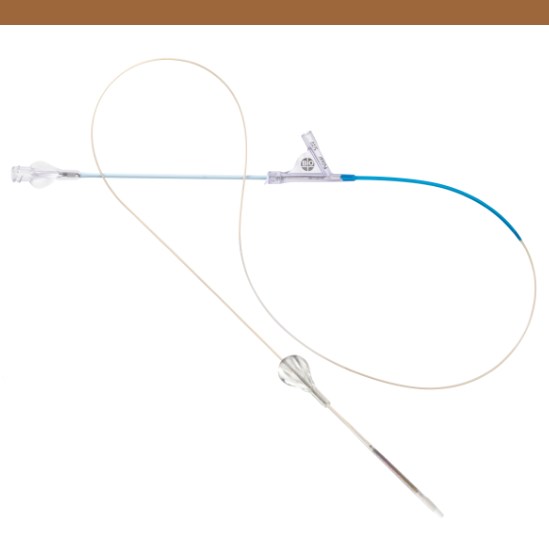
Product Details
Clinically Proven in Mid-Term Follow-Up (24 months)
Pulsar stents in shorter lesions:
4EVER1 trial. ALL 4.3 cm; PP 76.2%; FTLR 82.3%
REAP2 trial. ALL 5.2 cm; PP 68.0%; FTLR 86.2%
Pulsar stents in combination with Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB):
DEBAS3 trial. ALL 18.8 cm; PP 88.2%; FTLR 91.0%4

Stent Designed for SFA
- Peak-to-valley design and S-articulating connecting bars provide multi-directional flexibility and avoid fish-scaling in mobile vessel architecture.
- A segmented stent design with thin struts provides low chronic outward force (COF)5 sufficient to maintain vessel scaffolding even in calcified lesions (4EVER trial1). High COF has been shown to result in higher rates of neointimal hyperplasia.6, 7, 8
- Ideal for shorter lesions, spot-stenting or combination therapy with DCB
Pull-Back Delivery System
Enables simple stent deployment.
Safety Tab
Avoids accidental stent deployment.
Easy Release
Relieves friction of introducer valve on the rectractable shaft during stent deployment for a smoother action.
Low Profile Delivery System
4 F distal shaft profile for easier lesion crossing. 3.6 F proximal shaft for contrast injection with device positioned inside introducer and across lesion.
4-EVER
- Physician-initiated trial investigating the safety of the full 4F endovascular treatment approach of infra-inguinal arterial stenotic disease.
- Number of patients (n): 120
- Primary endpoint: Primary Patency (PP) at 12 months
Technical Data
| Astron Pulsar Stent | |
|---|---|
| Catheter type | OTW |
| Recommended guide wire | 0.018" |
| Stent material | Nitinol |
| Strut thickness | 155 μm |
| Stent coating | proBIO (amorphous silicone carbide) |
| Stent markers | 6 gold markers on each end |
| Sizes | ø 4 - 7 mm; L: 20 - 80 mm |
| Proximal shaft | 3.6 F, hydrophobic coating |
| Usable length | 70 cm (ø 5.0 - 7.0 mm) 72 cm (ø 4.0 mm, L: 60 - 80 mm) 75 cm (ø 4.0 mm, L: 20 - 40 mm) 120 cm (ø 5.0 - 7.0 mm) 130 cm (ø 4.0 mm, L: 60 - 80 mm) 135 cm (ø 4.0 mm, L: 20 - 40 mm) |
Ordering Information
Contact
1 4EVER trial. Bosiers. M. 24m results presented at CIRSE 2013; Deloose K. 24m results presented at LINC 2014.
2 Acín. F. et al. Astron Pulsar Nitinol stent in the femoropopliteal sector. Técnicas Endovasculares 2010; 13: 3203-3211.
3 DEBAS trial. Mwipatayi P. 24-month results presented VEITH 2015.
4 DEBAS uses Pulsar-18 stent, another member of the Pulsar family with similar stent characteristics.
5 BIOTRONIK data on file.
6 Ballyk PD. Intramural stress increases exponentially with stent diameter: a stress threshold for neointimal hyperplasia. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006 Jul; 17(7): 1139-45.
7 Freeman JW, Snowhill PB, Nosher JL. A link between stent radial forces and vascular wall remodeling: the discovery of an optimal stent radial force for minimal vessel restenosis. Connect Tissue Res. 2010 Aug; 51(4): 314-26.
8 Zhao HQ, Nikanorov A, Virmani R, Jones R, Pacheco E, Schwartz LB. Late stent expansion and neointimal proliferation of oversized Nitinol stents in peripheral arteries. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009 Jul; 32(4): 720-6.